Node-RED is a programming tool for wiring together hardware devices, APIs and online services in new and interesting ways.
It provides a browser-based editor that makes it easy to wire together flows using the wide range of nodes in the palette that can be deployed to its runtime in a single-click.
Get started
First, update your RuuviTags to the latest firmware and put the tags into the RAW mode.
We have made a Node-RED node which listens to incoming Bluetooth advertisements using Node-RED-Noble and parses data from the advertisements.
Install the Node-RED node as instructed on GitHub. Instructions for adding a node to NPM (package manager) are coming up later.
Noble runs on macOS and Linux, so you need to have a Bluetooth Low Energy enabled computer with either OS. Linux + VirtualBox will work fine with a USB Bluetooth dongle. You can also use a Raspberry Pi 3 which has both WiFi and Bluetooth integrated.
How does it work?
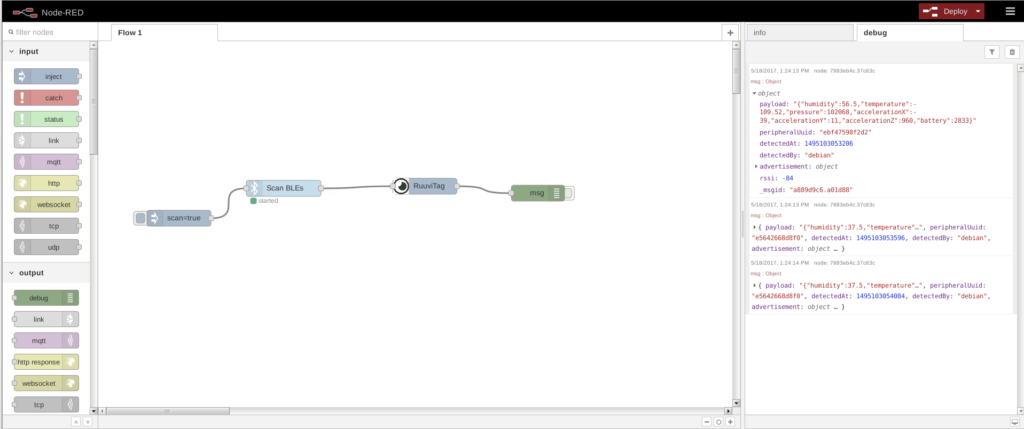
Our node receives Bluetooth advertisement data from Noble node.
Note that in order to output data values which are updating correctly, you need to allow duplicates.
Connect the output of the Noble node to the input of the RuuviTag node. This way RuuviTag will output JSON that contains the sensor readings.
What can I do with it?
A lot of IoT systems have their own Node-RED nodes available. You can connect the RuuviTags to these supported systems. To get started, please refer to the Node-RED guide.
Contributed nodes are named “node-red-contrib-xxx” by default, where “xxx” is the name of the technology used. Usually, the fastest way to find if the technology you want to use is supported by Node-RED is to search keywords “node-red-contrib-tech”.
Tell us…
How did you use the node? We’re sure others would love to know!