Even though it may sound like a solution for industrial agriculture, a smart greenhouse can work for everyone, even in your small garden or on your balcony. In this article, discover what a smart greenhouse is all about and how to get started with it.
Definition, origins and differences between a smart greenhouse and a conventional greenhouse
A smart greenhouse uses monitoring and control systems to optimise growth conditions of plants.
Greenhouse automation is getting more accessible and cheaper
Smart technologies and greenhouse automation are finding their way from industrial uses to the individual consumer market. For example, automatic fans and heaters, vents that open and close in response to the temperature, and computer-controlled watering systems that provide water and fertilizers are readily available for both commercial gardens as well as domestic greenhouses.
One good sensor for both the beginner and advanced grower is RuuviTag! Check below a video about how it works.
In recent years, sensor-driven automation has branched out from factories and laboratories into our homes and everyday lives. So it’s no surprise that technology is slowly finding its way into our gardens and making greenhouses smarter, too.
Smart sensors play a key role
Smart actuators, sensors, and monitoring systems are at the heart of the new green movement in cities. As a result, people are finding new ways of growing clean foods within their communities and limited spaces. And it’s not just for the tinkerers! All you need to get started is a smartphone and a specialised sensor, such as the RuuviTag.
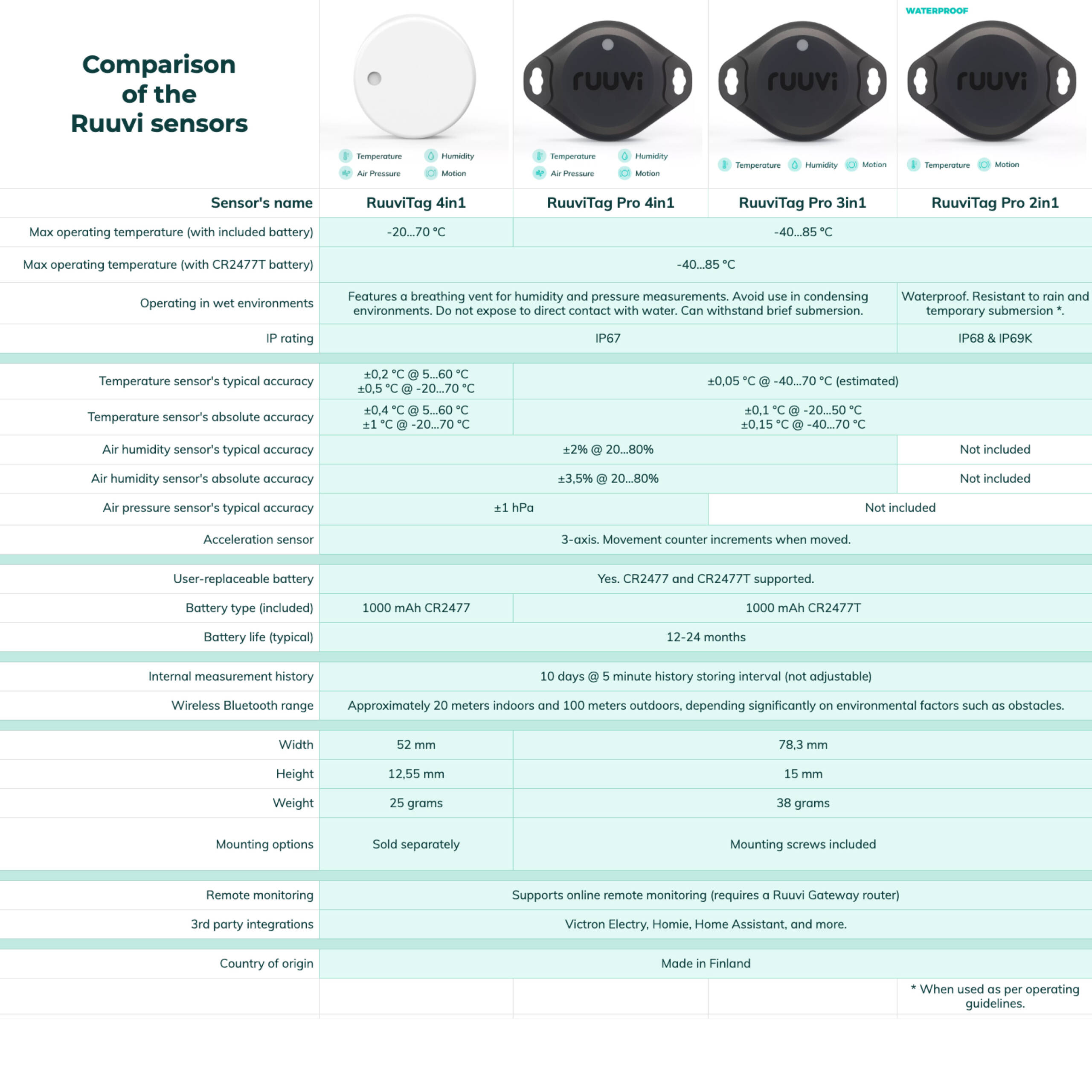
RuuviTag is an advanced open-source sensor that fits perfectly in greenhouse applications.
The short history of greenhouses
The idea of growing plants in environmentally controlled areas has existed since ancient Roman times. The first modern greenhouses appeared in Europe in the 17th century. These private greenhouses were mainly built by the rich and educated, to grow and study plants that were imported from tropical parts of the world.
These greenhouses, however, were not very practical; they were expensive to build, required a lot of work to operate, and provided many challenges in maintaining constant heat and ventilation. As materials and building techniques improved over time, greenhouses became more and more efficient and practical to use.
The last century has seen many technological advances, such as the invention of large sheets of polyethylene, that have allowed greenhouses to become even more cost and energy-efficient while gradually making their way into homeowners’ gardens, backyards, and even balconies.
Today, a large percentage of greenhouses are still built using poly sheets, aluminum extrusions, galvanized steel tubing, and PVC water pipes.

What are the advantages of automated greenhouse systems?
A simple backyard greenhouse doesn’t necessarily need automation, such as computer-controlled shades, irrigation, ventilation, or temperature control.
However, it’s important to understand that maintaining controlled temperature and humidity within a greenhouse are two of the most important elements of any functional greenhouse. Extreme temperature fluctuations may have a significant impact on the plants’ health and an overheated greenhouse can also cause the soil to dry out quicker and increase water usage.
Humidity affects a plant’s ability to perform its core biological functions. Plants use a process called transpiration, which helps move water used for photosynthesis and growth. It also plays a significant role in cooling the plant. Too much humidity, however, can result in bacterial and fungal infections, so finding the right balance is imperative to plant health. Monitoring and controlling both temperature and relative humidity locally or remotely becomes extremely important.
This might be interesting for you
>> Smart greenhouse monitoring on a budget
What sensors are used to monitor plant growth?
There are many different types of sensors available for smart greenhouses that measure and report data for environmental monitoring and for controlling automation.
- Humidity sensors
- Temperature sensors
- Soil moisture sensors
- Light sensors
- Soil PH Sensors
- Air quality sensors
- Carbon dioxide sensors
Your choice of equipment should be capable of handling the greenhouse environment. Those typically requires special attention with electric power supplies and sensors that might be sensitive to water splashes, sunlight, and humidity. A successful solution should be greater than the sum of its parts.
How To Easily Monitor Greenhouse Humidity Levels?
Monitoring greenhouse temperature and humidity is easy with the use of smart sensor technology. A simple way to monitor greenhouse temperature and humidity is to place at least three sensors inside the greenhouse. One at each end of the structure and one in the middle.
Thermometer or smart sensor?
The simplest measurements can be taken by using a digital thermometer. But opting for a more advanced sensor might prove more practical. Having real-time environmental data available on your mobile phone could be a real life-saver in case of equipment failure requiring immediate attention. Also, some plants are very sensitive to sudden changes in temperature. Therefore having access to real-time data can help you save your yield.
It has been suggested that advanced temperature monitoring should involve measuring air temperature, growing media temperature, and plant temperature separately. In this case, using advanced systems such as computer-operated infrared sensors or other smart sensors becomes a necessity.
Building your own Arduino greenhouse automation DIY project
It goes without saying that the more advanced automation and monitoring systems are always going to be geared towards commercial use. However, community gardens and community-driven greenhouse projects could benefit from open source-based solutions, such as Raspberry Pi or Arduino platforms.
It’s easy to find complete instructions to build anything from automated elements to fully automated greenhouses. These greenhouses include automatic monitoring, watering, and ventilation. It shouldn’t take a beginner more than a couple of days of watching YouTube videos and online tutorials to learn everything you need to know about building a smart greenhouse from scratch.
Using the RuuviTag smart Bluetooth sensor to monitor your greenhouse
As appealing as building your very own system might sound, the level of technical understanding required in this approach could be a big turnoff for many. RuuviTag is among the few wireless sensors that both beginners and advanced users can use. The sensor can function as an independent mobile-ready weather station right out of the box, or you can use as many RuuviTag sensors as you need to support a full-blown industrial sensor grid.
RuuviTag is a wireless sensor that sends temperature, relative air humidity, air pressure, and motion information directly to your mobile phone. The sensor even comes in a weatherproof enclosure, which makes it extra appealing for greenhouse applications.
Ruuvi Gateway is our solution to have your greenhouse monitored constantly. Ruuvi Gateway listens to RuuviTag’s measurement broadcasts and sends them to Ruuvi Cloud. There you can read your RuuviTags’s data at all times as long as you have a working internet connection. With Ruuvi Gateway, you can receive alerts if anything unwanted happens in your greenhouse at any time.

Greenhouse environmental monitoring with alerts
No one can sit and monitor a greenhouse’s conditions all the time. That is why you need an environmental monitoring system that can ensure that correct conditions are met at all times.
Ruuvi is a great alternative to greenhouse monitoring. You may place Ruuvi’s sensor in the greenhouse. Once it is active, you can set up alerts on the Ruuvi Station on mobile or desktop.

Which alerts should you set for the greenhouse?
Set lowest temperature alert to 16 °C and highest temperature to 26 °C.
Set lowest relative humidity to 30% and highest relative humidity to 60%
These are the optimal levels for plants. By setting these alarms, you will know instantly if the conditions are not optional. With Gateway, you will receive an email stating that the conditions are not optimal.
Optional alerts for smart greenhouse monitoring systems
RuuviTag has a barometer built inside of it. Barometer can help to identify changes in weather. By monitoring changes in your local barometric pressure, you can be alerted if a storm is on the way. This way you can cover up your greenhouse better.
Also, you can set an alert for movement. You can place RuuviTag on the door of the greenhouse. Once the door opens, you will receive an alert. Pretty handy, if you want to keep your plants protected from kids or animals who would cause damage to fragile plants.
Taking smart greenhouse to a new level
As RuuviTag has a three dimensional accelerometer, you can take advantage of it in a smart greenhouse. Earth is pulling the Tag constantly to its mass centre. This force is equal to roughly 1G. If you have RuuviTag in a door or a hatch, you can read from the acceleration measurement Tags position toward earth.
This is useful if you want to see when automated ventilation or irrigation systems work.
In Conclusion
If you would like to grow your own fresh produce or want to take your plant growing interest to a new level, you should think about upgrading your greenhouse to a smarter one to help you get the best results. Thanks to technological advances, smart Bluetooth sensors such as RuuviTag are very affordable and work straight out of the box. In addition, for those looking for an additional challenge, both the sensor and the mobile app are 100% open-source, offering you the ideal opportunity to build your own smart greenhouse solutions.
Buy RuuviTag And Improve Your Greenhouse
Make your greenhouse smarter instantly with RuuviTag!
39,90€
Ruuvi is based in Finland. If you’re an EU consumer, VAT is included. If you’re a non-EU customer, you don't pay VAT. If you're an EU business, insert your VAT ID at checkout.
In stock
RuuviTag Sensor (4in1)
| Quantity | Unit Price(€) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 39,90 |
| 2 | 37,40 |
| 3-5 | 36,90 |
| 6-8 | 35,90 |
| 9-12 | 34,90 |
| 13-25 | 33,90 |
| 26-99 | 32,90 |
Are you looking for bigger quantities? Contact us for pricing.
FAQ
Which sensors are used in greenhouses?
Most typical sensors in greenhouses are:
- Humidity sensors
- Temperature sensors
- Soil moisture sensors
- Light sensors
- Soil PH Sensors
- Air quality sensors
- Carbon dioxide sensors
What is a smart greenhouse?
For example automatic fans and heaters are convenient tools for any greenhouse. Also, computer controlled water and fertilizer providers are already available for almost anyone!
How to monitor greenhouse humidity levels?
Monitoring greenhouse’s humidity levels is made easy by inexpensive wireless Bluetooth sensors. RuuviTag is a great example of a adequate sensor.
What are the most important elements of any greenhouse?
The most important elements are maintained temperature and humidity.
What is a greenhouse monitoring system?
A greenhouse monitoring system is a collection of sensors, software, and hardware designed to measure and record environmental variables within a greenhouse. This system is used to monitor and optimize growing conditions, including temperature, humidity, CO2 levels, light intensity, soil moisture, and nutrient levels.